Real Health Photos – National Safety Month
For 100 years, the National Safety Council has been the leading safety advocate preventing unintentional injuries and death in the United States. The Council’s National Safety Month, Observed annually in June, focuses on reducing leading causes of injury and death on the job, on the road, in the home, and in all communities. Specific areas they address include workplace violence prevention, safe driving, poisoning prevention, ergonomics, and fall prevention.
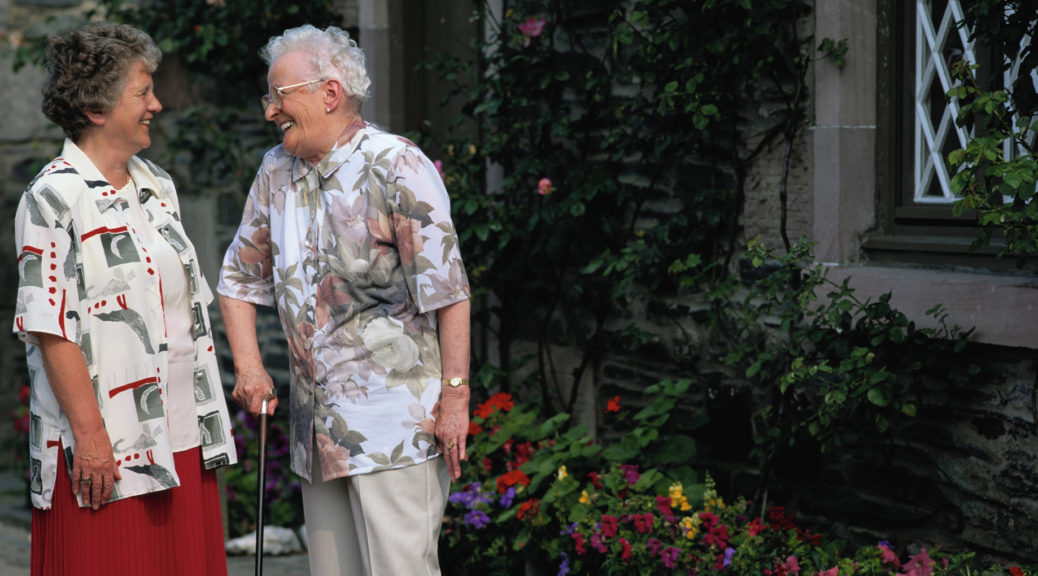
More than 33,000 people, for example, died in falls in 2015, according to the National Safety Council. “Falling is the third leading cause of unintentional injury-related deaths over all age groups, but it’s the #1 cause of death for those 65 and older” (Injury Facts 2017, National Safety Council). Strategies for preventing falls include securing carpets to the floor, wiping up spills immediately, installing grab bars in tubs, in showers, and near toilets, and if necessary, provide personal walking devices, such as canes or walkers, to aid in stability.
Klein Buendel’s Real Health Photos stock photography enterprise includes numerous images of older adults using personal walking devices. These unique photographs can be used in educational materials to show older adult populations how easy and typical it is for people to use devices for safe walking.
Real Health Photos images show a diversity of gender, race, ethnicity, age, income level, and health condition. Use Real Health Photos for improving the impact of health campaigns for people from all walks of life, including older adults.




For more images, visit Real Health Photos.
Real Health Photos is a stock photography service owned and operated by KB. It was created and evaluated with a research grant (R44MD003338, Mary Buller, Principal Investigator) from the National Institute of Minority Health and Health Disparities at the National Institutes of Health. Real Health Photos is designed to capture the diversity of health through photography and promote the inclusion of all populations in health promotion materials and media.
Real Health Photos® is a KB registered trademark.